Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillators or ICD is a procedure used for the treatment of irregular heartbeats, or unrhythmic heartbeats. And ICD is a machine that monitors heartbeat and when it detects abnormality, pushes electric energy to get it to normal. People who are at the risk of a cardiac arrest, or those who have had a heart attack, might be asked to go through an ICD.
Overview
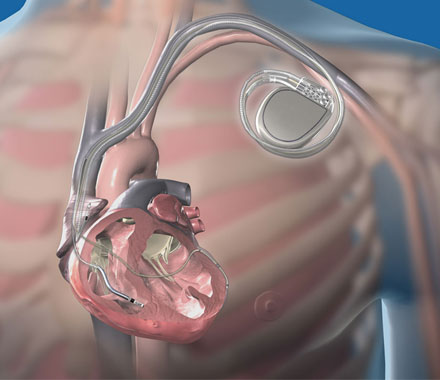
Like a pacemaker, the ICD also is a two part device make up of lead/s and pulse generator. The leads are wires and sensors that keep a check on the heart’s activity and delivery electric waves to normalize heartbeats as and when necessary. The generator holds a tiny programmable computer and a battery that stores electrical energy.
An ICD might perform one or all of these functions on your heart, depending on what the heart specialist finds necessary:
- Cardioversion, which is a process where a gentle electric shock is delivered to the heart through the leads to get the heartbeats back to normal.
- Antitachycardia Pacing (ATP) is a process which is used when the heart beats faster than usual. Rhythm is restored through electrical waves.
- Defibrillation is a process of delivering electric shocks to your heart when it beats dangerously fast.
- Bradycardia pacing is a process whenelectrical impulses are used on your heart when it runs too slow.
Before the treatment
How is it performed
Before the ICD planting procedure which takes about 5 hours, an IV line will be attached to your arm through which you will receive medicines and fluids. The medicines will keep you drowsy during the process and your heartbeat and blood pressure will be constantly monitored. One side your chest will be shaved and cleaned with an antiseptic for the procedure.
In the endocardial approach of ICD planting, which is the more common of the two ICD approaches, your heart specialist will make a tiny incision in the area under the collarbone. The lead, which are electric wires, are then put into your vein and then moved inside your heart chamber. Attached to the wires, the generator is then placed in the upper chest.
If the doctor instead goes for the epicardial approach, it require a more invasive open’heart surgery. In this approach the leads are attached directly to the heart, unlike the endocardial process where the leads travel through the veins.
Recovery
Usually, post the ICD your hospital stay would only be overnight. Your doctor will ask you to go through an X’ray next the morning after the process to make sure the leads are in set position and the ICD has been programmed properly. You will receive a temporary card detailing the types of leads that have been used in your ICD, the name of your doctor and the date of installing. After a few months, you will get a permanent card which can be used as a reference for medical help in the future.
You might be asked to not lift heavy weight for at least six weeks after the procedure. If your ICD was planted through the epicardial approach, then your recovery time will be longer. You will be told how to care for the wound.




Leave A Comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.