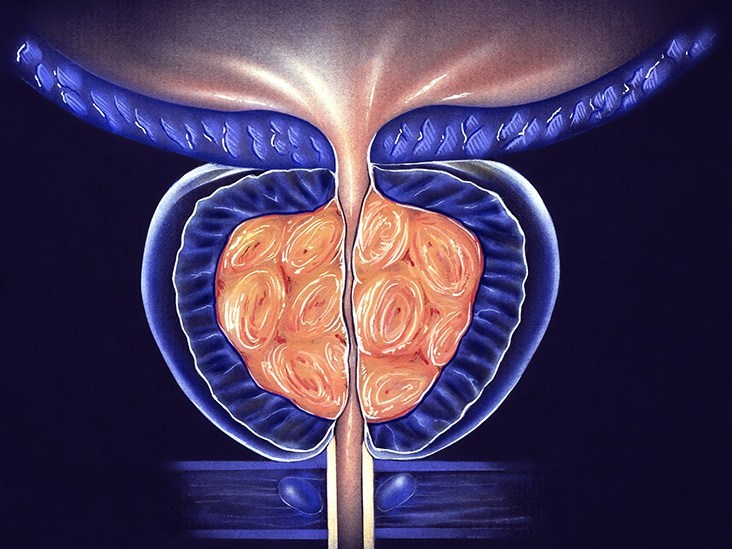
All men have a prostate, which is a walnut-sized gland. The position of it is in front of the rectum and below the bladder. The fluid that contains sperm (semen) is produced by the prostate. When the sperm travels towards a female’s egg, this fluid protects it. Prostatitis is that condition in which the prostate becomes swollen, tender and inflamed. It is different from having an enlarged prostate and it is also not cancer.
Symptoms
Prostatitis has four types, each of which has particular symptoms and causes. A urologist can confirm the type of prostatitis in any particular case after judging the symptoms.
Acute bacterial prostatitis:
Your kidneys, bladder and the tubes that pass through them make up the urinary tract. You can get an infection if bacteria from here find a way into your prostate. The symptoms are:
- 1] Muscle aches
- 2] A feeling of pain around the base of your penis or behind your scrotum
- 3] Lower back pain
- 4] Joint pain
- 5] Chills
- 6] High fever
- 7] Feeling the need for a bowel movement
- 8] Trouble while peeing
- 9] Weak urine stream
Consult a prostate specialist if you see these symptoms as acute bacterial prostatitis is a severe condition.
Chronic bacterial prostatitis:
In older men, this is more common. This can linger for several months and is a milder bacterial infection. After they’ve had a urinary tract infection (UTI) or acute bacterial prostatitis, some men may get it. In chronic bacterial prostatitis, the symptoms often come and go. Therefore, the chance of missing them is normal. The symptoms include:
- 1]In the middle of the night, there is often an urgency to urinate
- 2] Pain while urine discharge
- 3] Feeling of pain after ejaculation (release of semen at orgasm)
- 4] Pain in the lower back portion
- 5] Pain in the rectum
- 6] Behind your scrotum, there is a ‘heavy’ feeling
- 7] Semen having blood
- 8] A UTI
- 9] No urine coming out or urinary blockage
Chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome (CP/CPPS):
Among the different types of prostatitis, this is the most common one. Majority of the signs that are seen in bacterial prostatitis are also seen in this condition. However, in this type, no bacteria are found present with this type when tests are run.
The causes of CP/CPPS cannot be surely told by a urologist. Physical injury, nearby nerve damage and stress are a few triggers. A role may be played by chemicals in your urine or your past UTI. A number of immune disorders like chronic fatigue syndrome and irritable bowel syndrome have also been linked to CP/CPPS. A pain lasting more than 3 months in at least one of the body parts mentioned below is the main sign of CP/CPPS.
- 1] Penis (often at the tip)
- 2] Scrotum
- 3] The area between scrotum and rectum
- 4] The lower portion of your abdomen
- 5] The lower portion of your back
When you pee or ejaculate, you may also feel pain. You may have to pee more than 8 times a day or you might not be able to hold your urine. Another common symptom of CP/CPPS is a weak urine stream.
Asymptomatic prostatitis:
There is an inflamed prostate in men who have this type of prostatitis but there are no symptoms. If a blood test is done by your prostate specialist that checks the health of your prostate, you may come to know that you have it. No treatment is needed for asymptomatic prostatitis, but it can lead to infertility.