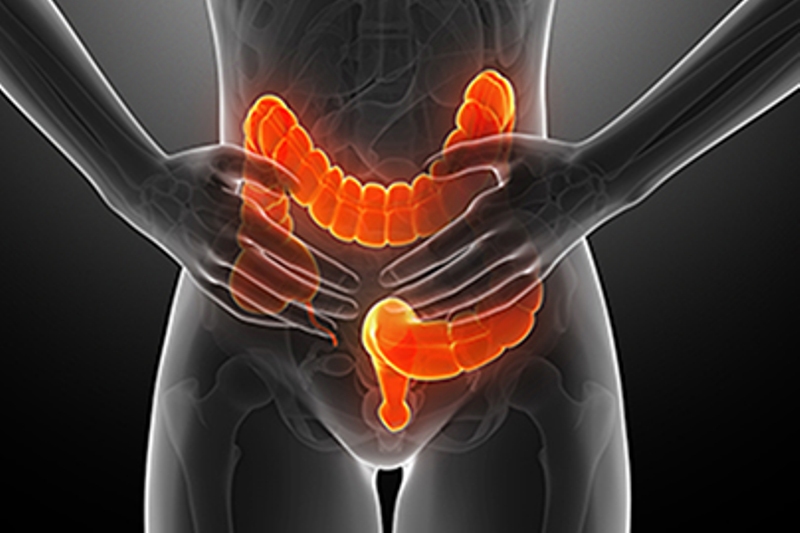
A type of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is known as Ulcerative Colitis. A long-lasting inflammation and ulcers develop in your digestive tract due to this. The innermost lining of the large intestine (colon) and rectum is affected by Ulcerative Colitis. There is not a sudden development of symptoms. They normally develop over time. Sometimes life-threatening complications can arise due to Ulcerative Colitis. The signs and symptoms of the disease can greatly reduce and there can even be long-term remission if treated properly by the best gastroenterologist, though it has no known cure.
Symptoms
Depending on the severity of inflammation and where it occurs, the symptoms of Ulcerative Colitis can vary. The following are some of its signs and symptoms:
-
Blood and pus mixed Diarrhea
-
Cramping and pain in the abdomen
-
Pain in the rectum
-
Stool having blood
-
Emergency need to defecate
-
Cannot be able to defecate even during emergency
-
Loss of weight
-
Feeling of fatigue
-
Fever
-
Lack of growth in children
There are mild to moderate symptoms in most people with Ulcerative Colitis. There may be variation in the course of Ulcerative Colitis as some people have long periods of remission.
Types
According to the location where it develops, a top gastroenterologist often classifies Ulcerative Colitis. The following are the different types of Ulcerative Colitis:
-
Ulcerative Proctitis:
In this case, the area closest to the anus is affected by inflammation and the only sign of the disease may be rectal bleeding. Ulcerative Colitis of this form tends to be the mildest.
-
Proctosigmoiditis:
The rectum and sigmoid colon (lower end of the colon) is affected by the inflammation. Bloody diarrhea, abdominal cramps and pain and inability to pass the bowels in spite of the urge to do so are some signs and symptoms of it.
-
Left-sided Colitis:
Through the sigmoid and descending colon, the inflammation extends above the rectum. Bloody diarrhea, abdominal cramping and pain on the left side and unintended weight loss are the signs and symptoms of it.
-
Pancolitis:
The entire colon is often affected by pancolitis and there may be severe bouts of bloody diarrhea, abdominal cramps and pain, fatigue and significant weight loss.
-
Acute Severe Ulcerative Colitis:
The entire colon is affected by this rare form of colitis and there is severe pain, profuse diarrhea, bleeding, fever and inability to eat.
Diagnosis
The best gastroenterologist uses a lot of tests and procedures to confirm a diagnosis of Ulcerative Colitis. Some of them are:
-
Blood Tests:
To check for anemia or for signs of infection, blood tests may be done.
-
Stool Sample:
Ulcerative Colitis and other disorders like bacterial infections can be indicated by white blood cells in your stool.
-
Colonoscopy:
A thin, flexible and lighted tube with an attached camera is used in this exam to view the entire colon.
-
Flexible sigmoidoscopy:
A slender, flexible, lighted tube is used to examine the rectum and sigmoid, the last portion of your colon.
X-ray, CT Scan, Computerized Tomography (CT) Enterography and Magnetic Resonance (MR) Enterography are some other diagnostic procedures.
Treatment
Either drug therapy or surgery is involved in the treatment of Ulcerative Colitis. Anti-inflammatory drugs, immune system suppressors and other medications are used.