Posterior urethral valve (PUV) disorder means an obstructive developmental anomaly in the urethra and genitourinary system of male newborn babies. A posterior urethral valve is an obstructing membrane in the posterior male urethra as a result of abnormal in utero development. This is considered by urology doctors as the most common cause of bladder outlet obstruction in male newborn babies. The disorder varies in degree, with mild cases followed conservatively. More severe cases can have renal and respiratory failure from lung underdevelopment as result of low amniotic fluid volumes, requiring intensive care and close monitoring. It occurs in about one in 8000 babies.
Classification
Posterior urethral obstruction was first classified by H. H. Young in 1919. The verumontanum, or mountain ridge, is a distinctive landmark in the prostatic urethra, important in the systemic division of posterior valve disorders:
- Type I – This is the most common type; due to anterior fusing of the plicae colliculi, mucosal fins extending from the bottom of the verumontanum distally along the prostatic and membranous urethra
- Type II – This is the least common variant; vertical or longitudinal folds between the verumontanum and proximal prostatic urethra and bladder neck
- Type III – This is the less common variant; a disc of tissue distal to verumontanum, also theorized to be a developmental anomaly of congenital urogenital remnants in the bulbar urethra
It is suggested that obstruction in the posterior urethra is more appropriately termed congenital obstructions of the posterior urethral membrane (COPUMs), a concept that has come from an in-depth analysis of the historical papers, and evaluation of patients with a prenatal diagnosis that has facilitated video recording of the uninstrumented obstructed urethra. The congenital obstructive lesions in the bulbar urethra, named Type III Valves by Young in 1919, have been eponymously referred to as Cobb’s collar or Moorman’s ring. For each of the COPUM (Posterior Urethra) and Cobb’s (Bulbar Urethra) lesions, the degree of obstruction can be variable, consistent with a variable expression of the embryopathy. The now nearly one hundred year old nomenclature of posterior urethral valves was based on limited radiology and primitive endoscopy, thus a change COPUM or Cobb’s has been appropriate.
Diagnosis
Abdominal ultrasound is of some benefit, but not diagnostic. As per urologists, features that suggest posterior urethral valves are bilateral hydronephrosis, a thickened bladder wall with thickened smooth muscle trabeculations, and bladder diverticula.
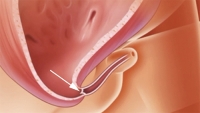
Voiding cystourethrogram (VCUG) is more specific for the diagnosis. Normal plicae circularis are variable in appearance and often not seen on normal VCUGs. PUV on voiding cystourethrogram is characterized by an abrupt tapering of urethral caliber near the verumontanum, with the specific level depending on the developmental variant. Vesicoureteral reflux is also seen in over 50% of cases.
Diagnosis can also be made by cystoscopy, where a small camera is inserted into the urethra for direct visualization of the posteriorly positioned valve. A limitation of this technique is that posterior valve tissue is translucent and can be pushed against the wall of the urethra by inflowing irrigation fluid, making it difficult to visualize.
Treatment
Treatment is by endoscopic valve ablation. Fetal surgery is a high risk procedure reserved for cases with severe oligohydramnios, to try to limit the associated lung underdevelopment, or pulmonary hypoplasia that is seen at birth in these patients. The risks of fetal surgery are significant and include limb entrapment, abdominal injury, and fetal or maternal death. Specific procedures for in utero intervention include infusions of amniotic fluid, serial bladder aspiration, and creating a connection between the amniotic sac and the fetal bladder, or vesicoamniotic shunt.
There are three specific endoscopic treatments of posterior urethral valves:
- Vesicostomy followed by valve ablation – a stoma, or hole, is made in the urinary bladder, also known as low diversion, after which the valve is ablated and the stoma is closed.
- Pyelostomy followed by valve ablation – stoma is made in the pelvis of the kidney as a slightly high diversion, after which the valve is ablated and the stoma is closed
- Primary (transurethral) valve ablation – the valve is removed through the urethra without creation of a stoma
The standard treatment is primary (transurethral) ablation of the valves. Urinary diversion is used in selected cases, and its benefit is disputed.
Following surgery, the follow-up in patients with posterior urethral valve syndrome is long term, and often requires a multidisciplinary effort between urologists, pulmonologists, neonatologists, radiologists and the family of the patient. Care must be taken to promote proper bladder compliance and renal function, as well as to monitor and treat the significant lung underdevelopment that can accompany the disorder.




Leave A Comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.