Laparoscopic Abdominal Hysterectomy uses minimally invasive procedure to remove the uterus. A tiny camera is inserted through a small cut in the lower abdomen to help the surgeon see the internal of the patient’s abdomen on the monitor while performing the excision. The potential candidates for laparoscopic abdominal Hysterectomy are those suffering from uterine fibroids or abnormal uterine bleeding.
Overview
Laparoscopic Abdominal Hysterectomy is a surgical procedure conducted with minimally invasive technique. This means two or three small incisions are made in the lower abdomen of the female patient. A tiny camera is inserted through one of the cuts and other specialized instruments are inserted through the other cuts into the abdomen to remove the uterus.
The ovaries and the cervix may not be removed during the Laparoscopic Abdominal Hysterectomy surgery. If the ovaries are not removed, then patients may not require taking any hormonal pills. There are two choices for patients with regards to the cervix, either to remove the entire uterus (which is called total laparoscopic hysterectomy) or keep the cervix intact (called supra-cervical hysterectomy).
The advantages of laparoscopic hysterectomy include lesser pain, quicker recovery, fewer incisions, lower risks of infections and blood loss, etc. Those who suffer from fibroids or abnormal uterine bleeding need to undergo laparoscopic abdominal hysterectomy. Before the surgery, there are some preparations to be taken as advised by the top gynaecologists, which has been discussed below:
Before the Treatment
Once a patient is recommended to get the surgery done, she has to take a few preparations before laparoscopic hysterectomy like checking with her primary care doctor, undergoing certain physical tests and following a few routine procedures the night before the surgery. Usually, the patient is asked to check with her primary care doctor to ensure that there are no medical conditions that may cause problems at the time of surgery.
An appointment is fixed on the day before the surgery. On this day, patients are asked to visit the doctor’s clinic so that a thorough physical examination is done and blood samples of the patient are tested. She is also asked to bring her medical history so that the gynaecologist can go through it to understand the types of medicines and treatments that can be given to her before, during and after the surgery.
A visit to the anaesthesia department is also necessary to have a talk to the anaesthesiologist to understand the type of anaesthesia that will be administered on the patient. She should not eat or drink anything starting from midnight on the night of the surgery.
How it is performed
Laparoscopic surgery is popularly known as Keyhole surgery. In contrast to an open surgery, laparoscopic abdominal hysterectomy is the most preferred treatment nowadays for removing the uterus, other organs and adjacent tissues present in the reproductive system. The following gives details of how surgeons perform laparoscopic surgery:
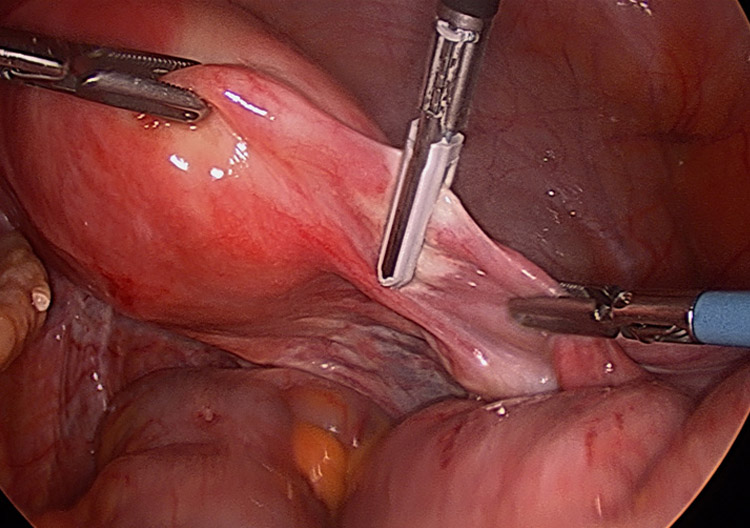
- Patients are usually administered general anaesthesia before the surgery. The procedure uses a minimally invasive technique to create a small incision in the belly button. A tiny camera is placed at one end of a small tube (called laparoscope), which is threaded through one of the cuts in the belly. The purpose of inserting a camera is to help gynaecologists view the inside of the abdomen on a monitor while performing the surgery.
- A couple of more incisions are done in the lower abdomen in order to insert instruments through them to cut the uterus in pieces and remove them through the small incisions.
- Else, the uterus can also be removed through a large incision in the belly. Sometimes, surgeons choose to remove the uterus through the vagina, which is also called vaginal hysterectomy procedure. In some cases, only the upper portion of the uterus is eliminated, keeping the cervix intact, while in others the entire uterus along with the cervix is cut out. The latter procedure is performed mostly to treat certain types of cancer, like cervical cancer.
- It should be noted that gynaecologists may remove tissues and other organs like the fallopian tubes or ovaries during the surgery, depending upon the medical requirement of the patient.
Recovery
After the surgery is performed, the patient wakes up to slight pain and exhaustion. She is kept on a catherter and a drip for one or two days. She is required to stay 2-5 days in the hospital. The doctor prescribes a few discharge medicines that the patient has to take.
Once discharged from the hospital, the patient is advised to follow a few hysterectomy recovery procedures while resting at home. She should try to stay mobile as much as possible, drink and eat normally, shower normally and use sanitary napkins (instead of tampons) if required. Activities like sexual intercourse and heavy lifting should be avoided for at least six weeks. However, the patient may experience vaginal discharge for a few days. She should take off from work up to six weeks after the surgery.
Post surgery, there is a lingering feeling of numbness around the wound, which is common and it may stay permanently. The most important fact is the patient won’t be able to menstruate or conceive post surgery. Thus, in overall, the recovery time of laparoscopic hysterectomy is approximately six weeks.


Leave A Comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.